What is NFC and How Does NFC Work? Comprehensive Guide
You’ve probably heard of NFC before and may even own a smartphone with that technology, but what is NFC on the phone?
In a nutshell, it is a proximity-based wireless communication standard. Unlike Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, however, NFC interaction is limited to a concise range. Besides smartphones, you can sometimes find NFC on tablets, speakers, collectibles, and even gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch and 3DS.
In this article, we’ll examine NFC and its functions. We’ll also explore where you’ll most likely encounter the technology in the real world.
What Is NFC?
Essentially, NFC stands for Near Field Communication; it’s a way for your phone to interact with something nearby.

When held nearby, NFC allows smartphones and other devices to communicate via radio signals. This allows for two-way communication, with both devices sending and receiving information.
Most people consider NFC’s small radius a significant security benefit, and it’s one reason why NFC has taken off as a secure alternative to credit cards. However, the technology can be used for more than buying coffee at Starbucks. NFC can also transfer data like videos, contact information, and photos between two NFC-enabled devices.
Devices with NFC hardware can establish communications with other NFC-equipped devices and NFC “tags.” NFC tags are unpowered NFC chips that draw power from a nearby smartphone or other powered NFC device. They don’t need their battery or source of energy.
An NFC communication system includes two separate parts: an NFC reader chip and an NFC tag. The NFC reader chip is the active part of the system; it “reads” (or processes) the information before triggering a specific response. It provides power and sends NFC commands to the passive part of the system, the NFC tag.
What is an NFC tag?

An NFC tag is a small integrated circuit with a copper coil and some storage. Data can be read or written to this tag only when another NFC device is brought near it because it doesn’t have a power source. The proximity of the NFC device induces power in the tag and enables data transmission.
NFC tags are small physical “tags” or “stickers” containing NFC chips that can be programmed to provide information to your smartphone.
Typically, an NFC tag contains links to a web address, but it can perform specific actions with your smartphone, like turning on the Wi-Fi or turning down the ringer. Where NFC presents an advantage over current QR technology is that there is no need for a “scanner app”: the information is immediately available.
In theory, these tags could be embedded into just about anything. For example, an NFC tag could be used in a restaurant menu to make the most up-to-date version available immediately on your phone. All you would need to do is bring your smartphone into proximity of the physical menu. You could then browse more detailed information about menu items, like nutritional values or ingredients.
How Do NFC Tags Work?
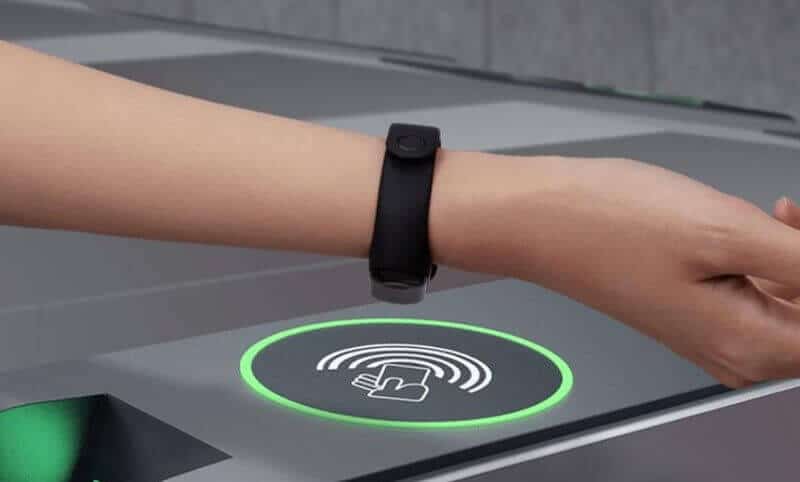

NFC tags work like any other RFID tag to communicate over radio waves—two devices — the NFC tag and the NFC reader exchange information in NFC data exchange format.
An NFC tag sends radio waves to activate the antenna in a receiving device. The recipient validates the information to complete the exchange. NFC tags work without a battery and draw power from another device, such as a smartphone.
What is an NFC reader?
Any powered device with its own NFC coil (like a smartphone or tablet) can act as an NFC reader. The reader device uses its battery to generate an electromagnetic field, which powers any tag brought near it. Another typical example of a reader is a payment terminal, which uses NFC to authenticate a debit or credit card.
How Does NFC Work?
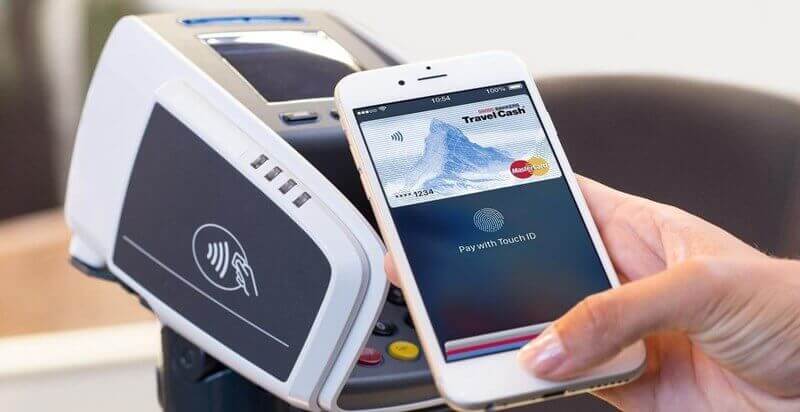

NFC isn’t some radically new technology. It’s simply an evolution of RFID (radio frequency identification) technology that has existed for decades. If you’ve ever used a key card to access an office building or hotel room, you’re already familiar with how it works.
NFC (near-field communication) enables two devices to communicate wirelessly when they’re close.
NFC is a subset of RFID (radio-frequency identification), a technology that allows us to identify things through radio waves. RFID is nothing new—it’s been used for decades to scan items in grocery stores, luggage on baggage claims, and cattle.
NFC, introduced in the early 2000s, uses a specific RFID frequency (13.56MHz, to be exact) for close-range communications. One of the more common uses for NFC is identification cards to access places like office buildings and private garages. But increasingly, NFC is being used to power so-called “contactless” payments.
If you’ve recently stood in line at large retailers like Whole Foods, Walgreens, or Office Depot, you’ve probably already seen a contactless payment.
What can you do with NFC?
NFC offers many opportunities for companies wishing to digitize experiences or facilitate access. Businesses all over the globe are using NFC for several use cases and applications. Here are a few popular use cases of the technology:
Mobile payments
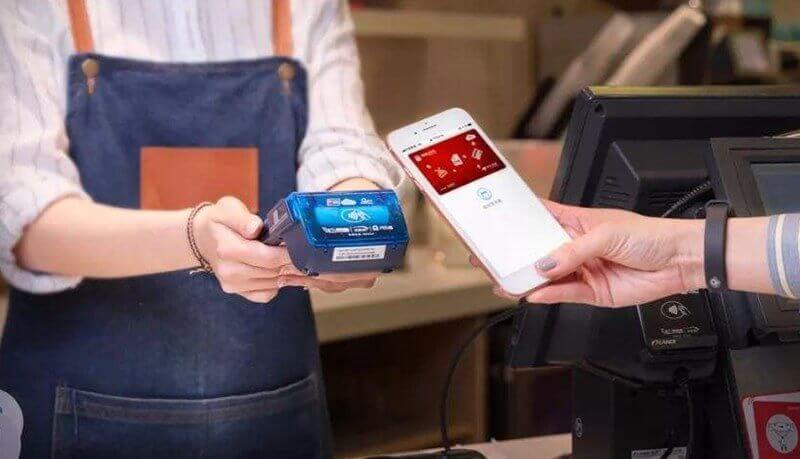

Mobile payments have become a popular transaction method as we gradually transition to a cashless world. The most common way consumers use NFC is to make tap-to-go payments. Leading payment services, including Google Play, Apple Pay, and Samsung Pay, use NFC for cashless payments in several countries worldwide.
Contactless payments are the most prominent use case for NFC technology. NFC makes transactions easy, secure, and fast — features coveted by consumers and businesses.
Consumers don’t need to input anything extra (PIN or signatures) for small transactions. Plus, NFC is a more secure way to pay — transactions happen instantly, and users don’t have to hand over their cards with sensitive information.
Ticketing

An NFC-enabled smartphone can be used as a ticket for concerts, movie shows, or even transit. Many businesses, operators, and public transportation services have added NFC technology to their ticketing operations.
For example, WMATA, the government agency that controls public transport in Washington, upgraded how commuters can use their SmarTrip cards. Now commuters can upload their card into their Apple Wallet and use their iPhone or Apple Watch to pay the fare.
NFC-enabled devices generate digital access tokens that people use to get on a bus or metro without needing to top up their SmarTrip cards. Payments will be made automatically using Apple Pay or Google Pay.
Identification and access control
NFC can identify team members and people who access select areas or floors. People can use their smartphones to open doors at the office — no separate access card is necessary for identification and access control.
Product status and maintenance
NXP, a manufacturer of semiconductors, has announced the launch of a new line of NFC-integrated circuits. The circuits provide a tamper-detection and condition-monitoring feature, which opens the doors to a host of new use cases for NFC tags.
For example, NFC circuits can be included in anti-tampering systems to detect tampering incidents on sealed products. When the cap is tampered with, the tag sends a signal to the chip’s memory, recording the breaking of the seal. The customer can later view the information via smartphone by scanning the product.
Connect with devices, wearables, and accessories.

Over the past few years, there has been a massive increase in the number of people using accessories that frequently connect to their smartphones for various purposes.
This is where NFC can come in handy. A single tap can establish the connection in seconds if both devices (your smartphone and the peripheral) support NFC. Some smartwatches and fitness ban models also support NFC for quick, hassle-free pairing.
Unlock car doors and homes.
A new use case for NFC, which debuted in 2020, lets users unlock car doors using an NFC-enabled smartphone. Apple announced the technology in collaboration with BMW and debuted with the 2021 BMW 5 series.
Instant connection
NFC devices connect instantly for data exchange when brought close together. The small range of NFC chips makes this valuable technology for payments, identification, access control, ticketing, or any other application requiring near-field data exchange.
Wireless exchange
All modern smartphones have NFC modules that connect wirelessly and without an external power source. NFC chips are passive devices powered by a device that reads them now (this happens through magnetic induction).
Secure, standardized, and regulated technology
NFC data exchange occurs only between devices nearby. A nearby connection limited to one device protects the transaction from hackers’ remote jacking.
NFC connections are regulated by standard protocols like ISO/IEC 14443 A, ISO/IEC 14443 B, and JIS X6319-4. ECMA International, ETSI, and other authorities ensure that NFC is universally secure and accessible across device vendors.
No need for network connectivity

NFC tags can work without Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G, or LTE connectivity. This means users can pay, transfer data, access areas, and use NFC-enabled services while disconnected from the internet.
Convenient and affordable technology
NFC tags are an easy and affordable technology that can help in digital transformation. Contactless payments, access control, and identification can significantly improve customer and employee experiences in their daily activities.
For example, you can use NFC to enable contactless access to your gym, health center, or office. Users can download your custom mobile app to pay for their membership and then use the smartphone to access the facility. In the post-COVID world, NFCs with digital tokens help any customer-facing business remain contactless.
Reduced carbon footprint
NFC is an eco-friendly solution that can minimize the carbon footprint of any business. Recyclable NFC tags made using paper reduce the use of plastic for access cards.
The same principle can unlock your home doors using your smartphone or an NFC-enabled key.
Which devices have NFC?

Most smartphones and wearables are equipped with NFC these days.
NFC has been a smartphone staple feature for several years. The Nexus S was the first Android device to include it in 2010. Apple also eventually embraced the technology in 2014 — NFC has been present on every iPhone since the 6.
Similarly, wearable devices, ranging from fitness trackers like the Mi Band to smartwatches like the Apple Watch, also include it.
Every iPhone since the iPhone 6
For a long time, Apple restricted NFC-equipped devices from making purchases. However, the latest iPhone models, including the iPhone 12, 12 Pro, 12 Pro Max, and 12 Mini, also support NFC tags through the Launch Center Pro app. Version 3 of the app includes NFC triggers for iPhone XR, XS, and XS Max for actions via custom NFC stickers. The iPhone 7 and newer phones can use in-app NFC scanning.
Every device running Android 4.0 and later.
If your device runs Android 4.4 or later, you can use Google Pay. You can also use Samsung Pay if you have a Samsung device.
Android phones operating on Android 4.4 to Android 9.0 can also use Android Beam for a message or file exchange. You can pass a lot of information to others, like YouTube videos, contact information, specific web pages, etc.
Does my smartphone support NFC?
Most high-end and upper-mid-range smartphones come with NFC support. However, Asian manufacturers like Xiaomi, Oppo, and Huawei have stopped shipping smartphones with NFC capabilities because of the market dynamics in countries where these famous brands have seen an increased preference for QR codes over NFC.
To find out if your phone supports NFC, go to Settings > Connected devices > Connection Preferences (on Stock Android) and see if there’s an NFC option hiding there.
Is NFC secure?

NFC mobile payments are dynamically encrypted, making them one of the most secure payment methods. NFC payments are incredibly secure — way more confident than magnetic-stripe cards.
Moreover, Apple Pay is protected by Touch ID, Apple’s fingerprint technology. You must unlock your phone via fingerprint to initiate an Apple Pay transaction.
So, even if your device is stolen, no one can get your data. (This is why Apple Pay only works on the most recent iPhone models equipped with Touch ID.)
NFC communication happens over the air, and there is no natural protection against eavesdropping and what is often referred to as man-in-the-middle attacks. However, these vulnerabilities are not such a big issue due to the proximity required for NFC to work.
After all, a thief must be within centimeters of your device to skim your data via NFC. If you use services like Google Pay and Apple Pay, you can rest assured that your credit card number is never transmitted. Instead, a digital account number is used to identify your payment details.
But there are several drawbacks as well. We have listed a few below:
- Not all smartphones support NFC.
- NFC has not found widespread usage in Asian markets where QR codes are still popular.
- NFC chips are not all located in the same place, resulting in some exploratory rubbing between devices.
- NFC is too slow for peer-to-peer file transfers, and newer, faster methods are now available.
What’s the difference between RFID and NFC?
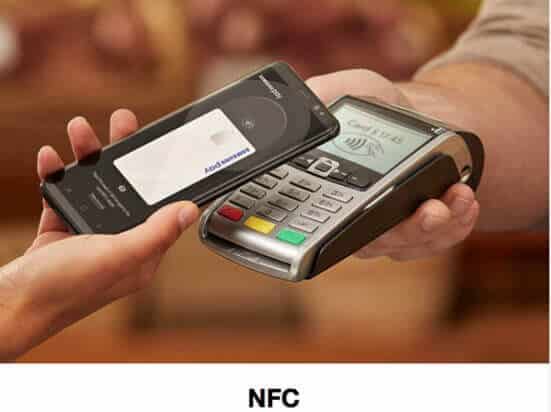

RFID and NFC operate on the principle of inductive coupling, at least for short-range implementations. The reader device generates a magnetic field by passing an electric current through a coil.
NFC is an evolution from the RFID technology, and both have specific use cases.
- NFC is very much like RFID, but NFC is limited to communication within about 4 inches, so you have to hold your phone close to the contactless reader if you’re using Apple Pay or Samsung Pay.
- Unlike RFID, NFC tags work nearby, giving users more precision. NFC also doesn’t require manual device discovery and synchronization like Bluetooth Low Energy. The most significant difference between RFID and NFC is the communication method.
- NFC devices can act as readers and tags, while RFID needs readers and labels separately. NFC and RFID can’t be directly compared because both have different applications. For example, NFC is widely popular for contactless payments, and RFID is more suitable for asset tracking.
- NFC offers a two-way communication channel, while RFID offers one-way communication., meaning an RFID-enabled item sends a signal to an RFID reader.
- So, RFID tags are great for inventory tracking, and NFC tags work well for enhanced communication.
NFC vs. Bluetooth and UWB: How do they stack up?

NFC is far from the only wireless communication protocol. Most devices include similar technologies, such as Bluetooth and ultra-wideband (UWB). So why have another?
- One of NFC’s biggest strengths is that it does not require pairing or manual input to establish a connection — tapping takes less than a second. Bluetooth devices, by contrast, have to be paired with each other, which is a cumbersome process.
- NFC is also significantly more energy-efficient than Bluetooth and UWB since the transmission range is concise. Most smartphones ship with the NFC radio enabled by default while turning off Bluetooth is often the first battery-conserving suggestion.
- NFC is less power-hungry and faster to use compared to Bluetooth.
- NFC’s lower power draw also allows specific devices like the iPhone to enable it in emergencies. This means that even if your phone runs out of juice, it will send just enough power to the NFC chip for you to access your campus, hotel room, or car.
- While cars are starting to adopt UWB tech for keyless entry, NFC is nowhere near as efficient. To that end, it’s unsurprising that many automakers implement the latter as a fallback access mechanism.
- UWB is also more expensive, and most applications currently served by NFC don’t need its positional precision.
EMV and NFC: What’s the difference?

You may hear EMV and NFC lumped together in discussions. That’s because they represent the next wave of more secure, authenticated payments (since they’re both encrypted to protect against counterfeiting). However, EMV and NFC are different technologies.
- Near-field communication (NFC) is associated with mobile contactless payments like Apple Pay.
- EMV® — developed and managed by American Express, Discover, JCB, Mastercard, UnionPay, and Visa — is associated with chip card payments.
- As a business, you’ll want to set yourself up to accept EMV soon. You’ll need a new point-of-sale terminal because chip cards are dipped instead of swiped.
- You can get a payment terminal that accepts EMV and NFC transactions to ensure you receive all the latest, most secure forms of payment from your customers.
- Both EMV and NFC are ‘authenticated’ payments.
Other Frequency asked questions.
What does NFC stand for on my phone or other NFC device?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. The technology allows wireless data transmission over short distances using radio waves.
How do I turn on NFC on an iPhone?
You don’t have to turn on NFC on an iPhone. iOS will automatically toggle NFC for applications like Apple Pay whenever required.
How do I turn on NFC on an Android phone?

Head into the Settings app and look for NFC under the “Connected Devices” or “Network and Sharing” sub-menus. Alternatively, you can use the search function in your settings.
How do I turn off NFC on my iPhone?
You cannot explicitly turn off NFC on an iPhone. The feature is always on by default. The good news is that it consumes very little battery, so there’s not a lot of benefit to turning off NFC like you would with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
How do I turn off NFC on Android?
You can turn off NFC on Android by flipping a toggle in the Settings app. Look for NFC under the ‘Connected Devices’ or ‘Network and Sharing’ sub-menus. Alternatively, you can use the search function.
What are NFC mobile payments?
Your smartphone can use NFC to mimic a contactless debit or credit card using apps like Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and Apple Pay. Payment terminals use NFC, so your smartphone emulates the data stored on your card. Only the account holder can add their card because the process involves authentication with the bank.
All of today’s smartphones are equipped with NFC technology. Whether you realize it or not, your phone is likely using NFC. But don’t worry — NFC uses minimal battery and processing power while offering various benefits that improve your device’s functionality.
How do I accept NFC?
You’ll need a new NFC-enabled payments reader that can accept contactless payments. The Square contactless and chip reader accepts both NFC and EMV payments.
Are NFC point-of-sale systems expensive?
Not necessarily. Some can be hundreds of dollars, but Square’s NFC-enabled reader is just $49.
How close do you have to be for NFC to work?

NFC works effectively within a 4-inch radius. Devices must be within this range for NFC to work. Such proximity makes NFC safer and more secure than similar technologies for contactless payments.
How can I increase the NFC range?
NFC is meant for communication with nearby devices. The range of NFC tags cannot be increased. Other technologies have more extensive ranges (e.g., Bluetooth Low Energy, RIFD, or ultra-wideband).
Are NFC payments secure?
Yes. NFC payments are more secure than paying via other mediums. Tokenization and encryption protect you from unauthorized costs and access.
What are the benefits of NFC payments?

NFC payments are easy and quick. You don’t need to carry a card or wallet to buy anything — you can use an NFC-enabled smartwatch, for example. Plus, NFC works with existing infrastructure, so there’s no need to invest in costly POS (point-of-sale) system upgrades.
NFC, or near-Field Communication, is a protocol that helps two devices communicate wirelessly when placed right next to each other. For instance, smartphones or smart watches can be used for payments or boarding passes. Here’s how it works.
NFC hardware is being included in more devices—particularly smartphones but also some laptops. NFC could be the future of payments, security keys, and boarding passes. It is also an upgrade over clunky QR codes. Many new phones have the hardware to do everything here today. However, many people with NFC-equipped smartphones haven’t used their NFC capabilities.